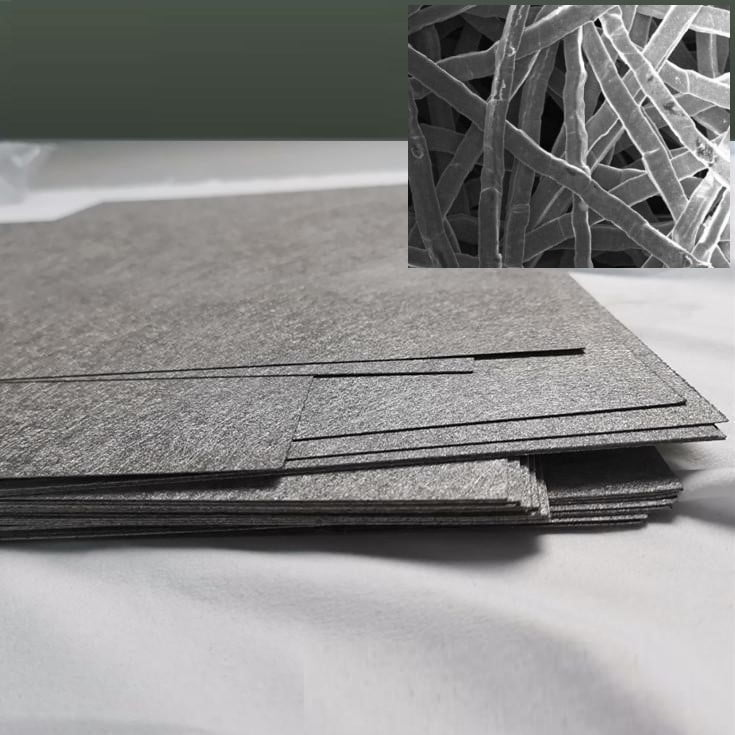
Hydrogen production technologies can be classified into several types, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. These technologies play a crucial role in the development of a hydrogen economy and the transition towards sustainable energy sources. Understanding the different types of hydrogen production technologies is essential for evaluating their potential impact on the environment, energy efficiency, and economic viability.
One of the most widely used methods for hydrogen production is steam methane reforming (SMR). This process involves reacting natural gas with steam to produce hydrogen and carbon monoxide. SMR is a mature and cost-effective technology that accounts for the majority of global hydrogen production. However, it is associated with greenhouse gas emissions due to the release of carbon dioxide.
Another prominent technology for hydrogen production is electrolysis, which uses electricity to split water into hydrogen and oxygen. Electrolysis can be powered by renewable energy sources such as solar or wind, making it a clean and sustainable option for hydrogen production. However, the high energy input required for electrolysis makes it less efficient compared to other methods.
Biomass gasification is another method for hydrogen production that involves converting organic materials into a gaseous mixture of hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and methane. This technology offers the advantage of utilizing renewable and sustainable feedstocks, but it requires careful management of by-products and waste streams to minimize environmental impact.
Photoelectrochemical water splitting is an emerging technology that uses semiconductor materials to directly convert solar energy into hydrogen fuel. This approach has the potential to achieve high efficiency and low environmental impact, but it is still in the early stages of development and faces challenges related to material performance and scalability.
Thermochemical water splitting is a process that utilizes high temperatures to decompose water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen. This method can be integrated with concentrated solar power or nuclear energy, offering the advantage of continuous operation and high-temperature heat utilization. However, it requires advanced materials and engineering solutions to achieve practical implementation.
Another innovative approach to hydrogen production is biological water splitting, which involves using microorganisms or enzymes to catalyze the conversion of water into hydrogen and oxygen. This method has the potential for low-cost and sustainable hydrogen production, but it requires further research and development to optimize biological catalysts and improve overall efficiency.
Overall, each type of hydrogen production technology has its own set of advantages and challenges. The selection of an appropriate technology depends on various factors such as resource availability, energy efficiency, environmental impact, and economic considerations. As the demand for clean and sustainable energy continues to grow, ongoing research and development efforts are essential for advancing hydrogen production technologies and accelerating the transition towards a hydrogen-based economy.