Introduction
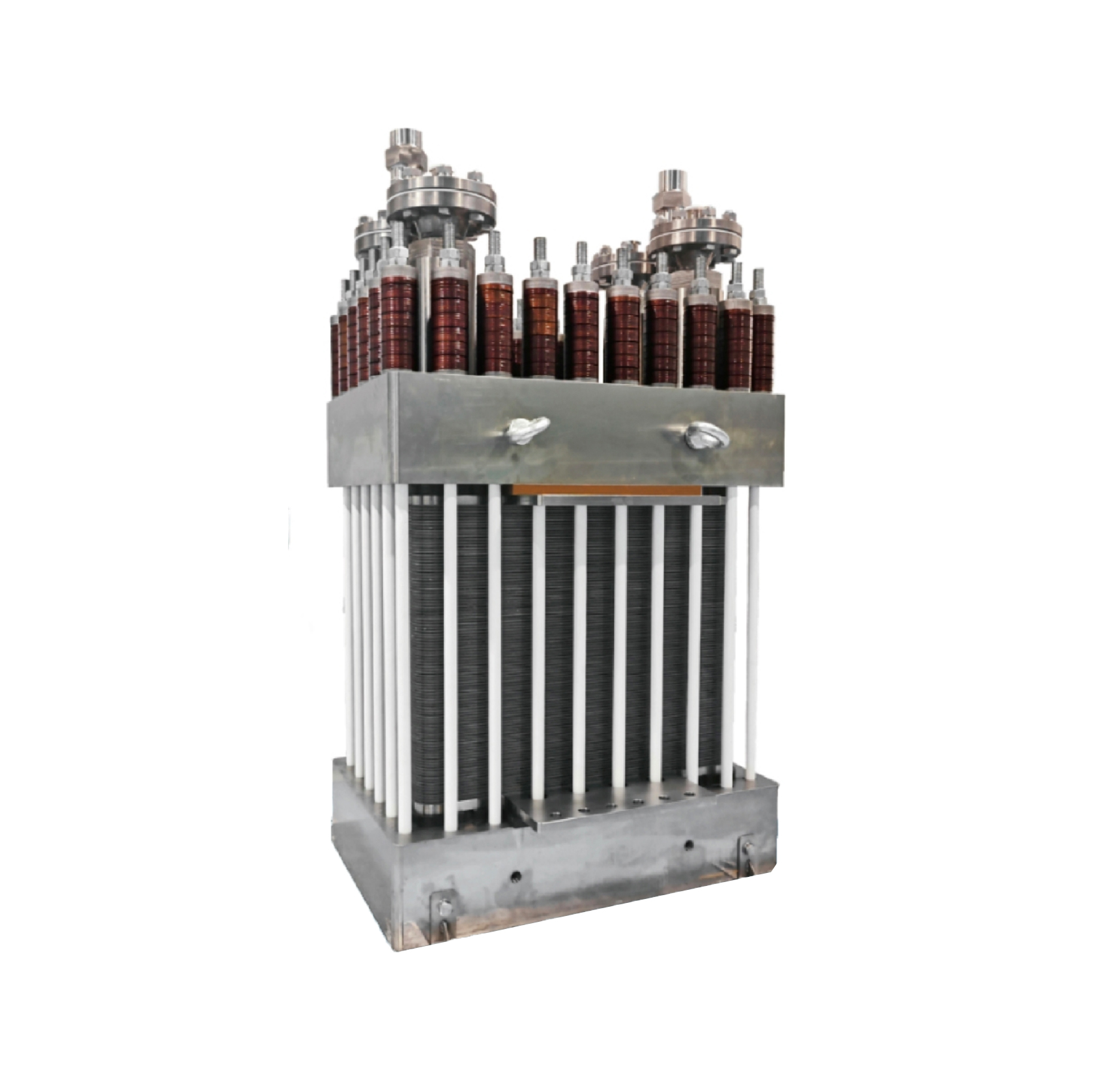
Green hydrogen, produced via electrolysis using renewable electricity, is seen as a cornerstone of the future clean energy system. Unlike gray or blue hydrogen, it generates zero carbon emissions, making it ideal for decarbonizing hard-to-abate sectors like steelmaking and long-haul transport.
Why Green Hydrogen?
- Decarbonization Potential:
- Replaces fossil fuels in industries where electrification is difficult.
- Enables renewable energy storage (power-to-gas).
- Global Initiatives:
- EU’s Hydrogen Strategy targets 40 GW of electrolyzers by 2030.
- Australia’s Asian Renewable Energy Hub aims to produce 1.75 million tons/year.
Challenges
- High Costs:
- Electrolyzer systems remain expensive.
- Renewable energy must be abundant and cheap.
- Infrastructure Needs:
- Requires new pipelines, storage, and refueling stations.
Future Outlook
With falling renewable energy prices and government support, green hydrogen could become cost-competitive with fossil-based hydrogen by 2030.